Introduction
GitHub Copilot has revolutionized how we write code, but did you know you can create custom chat modes to make it even more powerful? Custom chat modes allow you to create specialized AI assistants tailored to your specific needs - whether you’re working with particular frameworks, following specific coding standards, or need assistance with domain-specific tasks.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll walk through the process of creating custom chat modes for GitHub Copilot in VS Code, from basic setup to advanced customization techniques that will supercharge your development workflow.
Prerequisites
Before we dive in, make sure you have:
- Visual Studio Code installed
- GitHub Copilot subscription (individual or business)
- GitHub Copilot extension installed and configured
Visual Studio Code Setup
First, let’s ensure you have the GitHub Copilot Extension installed and properly configured.
Once installed, you can access the GitHub Copilot chat from the navigation bar on the left side of VS Code.
Understanding Chat Mode Locations
When creating custom chat modes, you’ll be prompted to choose between two storage locations:
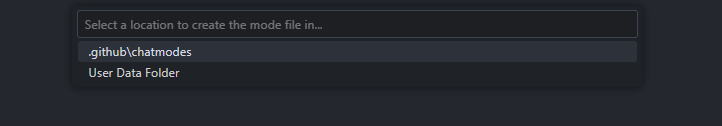
- Repository Specific: Custom modes are stored within your repository and shared with team members
- Workspace Specific: Custom modes are stored locally and available across all your projects
For team collaboration, repository-specific modes are ideal, while workspace-specific modes are perfect for personal productivity enhancements.
Locating the Prompts Directory
Custom chat modes are stored as markdown files in your VS Code user directory. You can find them at:
| |
On macOS/Linux, the equivalent path would be:
| |
Creating Your First Custom Chat Mode
Let’s create a practical example - a custom chat mode for Azure cloud architecture and PowerShell automation.
Step 1: Create the Prompt File
Navigate to your prompts directory and create a new file called azure-cloud-expert.md:
| |
Step 2: Advanced Customization
You can make your custom modes even more powerful by including specific instructions:
| |
Best Practices for Custom Chat Modes
1. Be Specific and Detailed
The more specific your instructions, the better the AI can assist you. Include:
- Exact Azure services and PowerShell modules you use
- Organizational naming conventions and tagging standards
- Preferred deployment patterns and architectures
- Common security and compliance requirements
2. Include Context Examples
Provide examples of the type of responses you expect:
| |
3. Define Response Structure
Specify how you want responses formatted:
| |
4. Version Control Your Prompts
If using repository-specific modes, commit them to version control so your team can benefit from shared expertise.
Practical Examples
Azure PowerShell Automation Mode
| |
Azure Solution Architect Mode
| |
Managing Multiple Custom Modes
As you create more custom modes, organization becomes important:
- Use descriptive filenames:
azure-expert.md,bicep-specialist.md,powershell-automation.md - Include version numbers in the metadata
- Document Azure service dependencies and prerequisites
- Regular maintenance to keep modes current with Azure updates and new services
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Mode Not Appearing
- Ensure the file is in the correct prompts directory
- Check that the markdown frontmatter is properly formatted
- Restart VS Code if the mode doesn’t appear immediately
Inconsistent Responses
- Make your instructions more specific
- Include more context about your preferred patterns
- Add examples of desired vs. undesired responses
Performance Issues
- Keep prompt files concise but comprehensive
- Avoid overly complex instructions that might confuse the AI
- Test your modes with various types of questions
Advanced Tips and Tricks
1. Chain Custom Modes
Create specialized modes that work together:
- An “Azure Architect” mode for designing cloud solutions
- A “Cost Optimizer” mode for analyzing and reducing Azure spending
- A “Security Auditor” mode for compliance and security assessments
2. Project-Specific Modes
Create modes tailored to specific Azure environments:
| |
3. Service-Specific Modes
Create modes for specific Azure services you work with regularly, such as Azure Functions, Azure Kubernetes Service, or Azure Cosmos DB.
Conclusion
Custom chat modes for GitHub Copilot are a powerful way to create specialized AI assistants that understand your specific Azure environment, cloud architecture standards, and operational requirements. By investing time in creating well-crafted custom modes focused on Azure and cloud technologies, you can significantly enhance your cloud development productivity and ensure more consistent, best-practice solutions.
Start with one or two focused modes for your most common Azure tasks, iterate based on your experience, and gradually build a collection of specialized cloud assistants that make you more effective in your daily Azure operations.
The key to success is specificity - the more context about your Azure environment, naming conventions, and architectural patterns you provide, the better your custom AI assistants will become at helping you build robust, secure, and cost-effective cloud solutions.