SSH (Secure Shell) is one of the most widely used protocols for securely accessing remote servers, and it’s no different for Azure Linux Virtual Machines (VMs). However, issues related to missing SSH keys can cause frustration when trying to authenticate and establish connections. This post will guide you through common causes, troubleshooting steps, and best practices for resolving SSH key issues on Azure Linux VMs.
Common Causes of Missing SSH Keys
Key Pair Not Properly Configured
When creating a new Azure Linux VM, it’s essential to associate a valid SSH key pair with the VM. If you skip this step or use the wrong key, SSH authentication will fail.
Corrupted or Misplaced SSH Keys
Sometimes, the SSH private or public keys may become corrupted or misplaced. This can lead to issues in authenticating the SSH session, preventing you from accessing the VM.
Permissions Issues
Improper permissions on the key files or the .ssh directory can also cause SSH authentication failures. Both the private key and the .ssh directory must have the correct access rights.
Incorrect Key Type or Format
SSH supports various key types (e.g., RSA, Ed25519). If the key format doesn’t match what the VM expects, authentication will fail. For instance, an RSA key might not work if the VM is configured to use Ed25519 keys only.
Troubleshooting Missing SSH Keys on Azure Linux VMs
Check the SSH Configuration
Ensure the VM is correctly configured with SSH and that the public key is properly placed in the ~/.ssh/authorized_keys file on the VM. You can verify this by logging in with a different user (if configured) or using a different method like serial console access.
Use Azure Serial Console
Important 🚨
If the virtual machine was created with SSH Keys initially, you wont be able to use the serial console, but will need to use the RunShellScript option
If you cannot access the VM via SSH, you can use the Azure Serial Console to troubleshoot further. It allows you to interact directly with the VM’s operating system, bypassing network-level SSH restrictions. This is especially helpful if the issue is related to key configuration.
Use Portal - RunShellScript
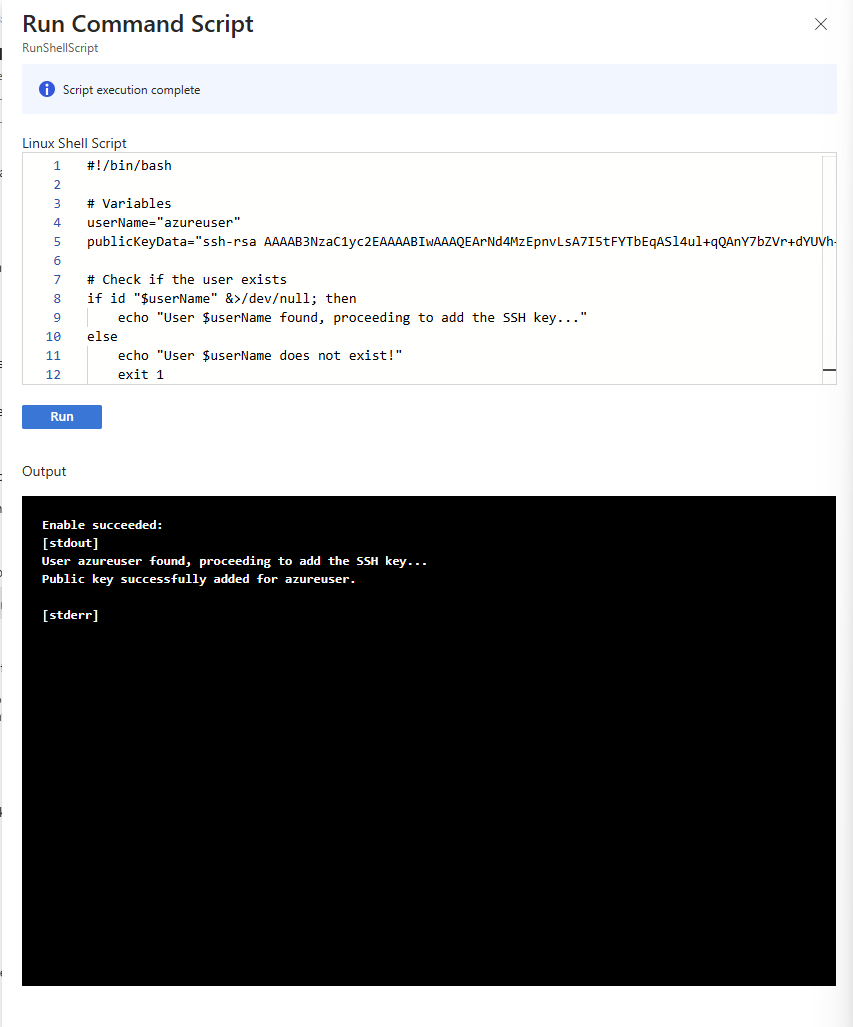
Using the RunShellScript, you can directly interact with the virtual machine, Using the following script we will pass in the new public key into the azuresuer local user.
Operations > Run command > RunShellScript
| |
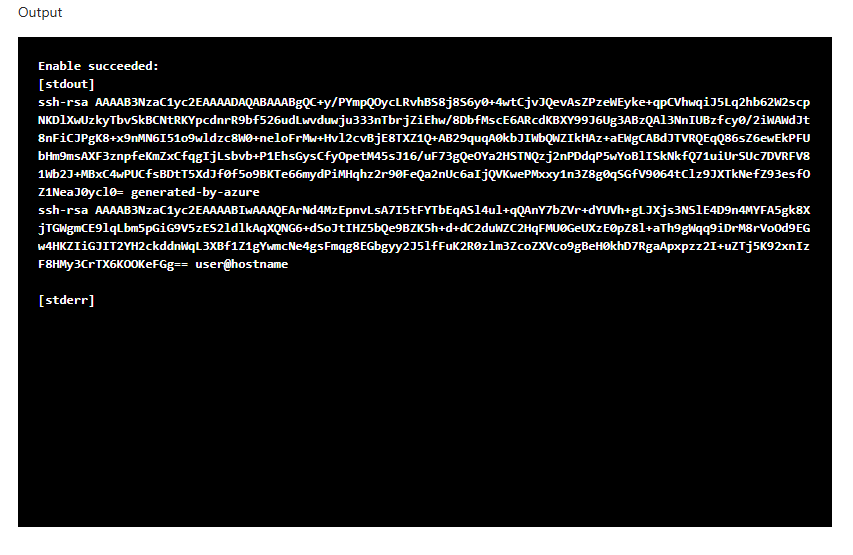
When we check the .ssh/authorized_keys we can see the key has been added. 🎉
Using AzureCLI
If the keys are missing or corrupted, regenerate them and update the VM configuration. Use the following commands to create a new SSH key pair:
| |
Once the new keys are generated, you’ll need to upload the new public key to the Azure VM. You can do this via the Azure Portal or Azure CLI:
| |
Verify Permissions: Ensure the correct permissions are set on the .ssh directory and the authorized_keys file. Use the following commands to set the appropriate permissions:
| |
Tip
| Permission Mode | Description | Effect |
|---|---|---|
700 | Set on the .ssh directory | - Owner: Read, write, and execute permissions (full access). - Group: No permissions. - Others: No permissions. |
600 | Set on the authorized_keys file | - Owner: Read and write permissions. - Group: No permissions. - Others: No permissions. |
Key Takeaways:
700ensures that only the owner can access the.sshdirectory.600ensures that only the owner can modify theauthorized_keysfile.
Confirm the Correct Key Type: Double-check that the key type and format are compatible with the VM’s configuration. If you’re unsure, regenerate the key pair using a common format like RSA, which is widely supported.
Best Practices for Securing SSH Access on Azure Linux VMs
Use Azure Key Vault for Key Management
To improve security and management of SSH keys, use Azure Key Vault to securely store and retrieve SSH keys. This ensures that sensitive keys are protected and can be managed centrally.
Enable SSH Key Authentication
Only Disable password-based authentication and enforce SSH key-based authentication. This reduces the risk of brute-force attacks and ensures that only authorized users can access the VM.
Limit SSH Access with Network Security Groups (NSG)
Use Azure Network Security Groups (NSGs) to restrict SSH access to specific IP addresses or ranges. This adds an extra layer of security by ensuring that only trusted sources can access your VM over SSH.
Use Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Whenever possible, enable MFA for SSH access using Azure AD authentication. This ensures an additional layer of security, even if the SSH key is compromised.
Regularly Rotate SSH Keys
Regularly rotate SSH keys to reduce the risk of unauthorized access. Automating key rotation and monitoring access logs can help ensure your environment remains secure.
Wrap Up
Missing SSH keys can cause significant issues when managing Azure Linux VMs, but with the right troubleshooting steps and best practices, you can quickly resolve these issues and improve the security of your infrastructure. Always ensure that SSH keys are properly configured, stored securely, and rotated regularly to minimize the risk of unauthorized access.
By following these guidelines, you can ensure a smooth and secure SSH experience when working with Azure Linux VMs.